

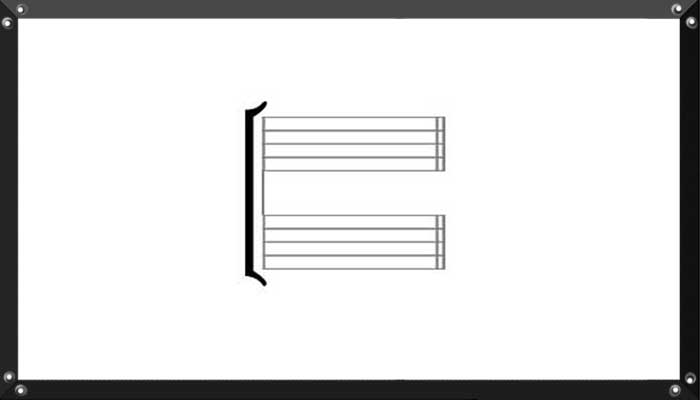
Connects two or more lines of music that sound simultaneously. In general contemporary usage the bracket usually connects the staves of separate instruments (e.g., flute and clarinet; two trumpets; etc.) or multiple vocal parts in a choir or ensemble, whereas the brace connects multiple parts for a single instrument (e.g., the right-hand and left-hand staves of a piano or harp part).
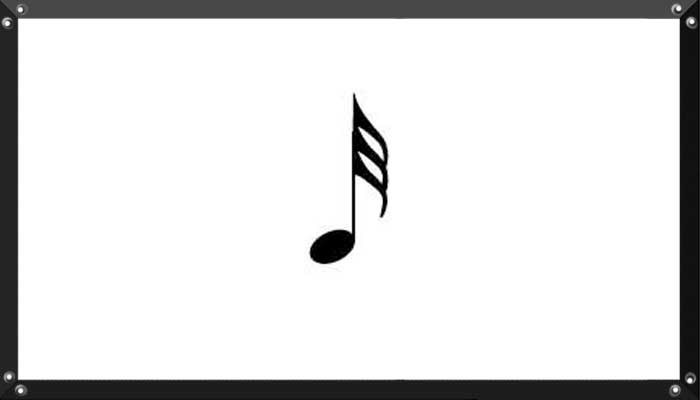

In music, a thirty-second note (American) or demisemiquaver (British) is a note played for 1⁄32 of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). It lasts half as long as a sixteenth note (or semiquaver) and twice as long as a sixty-fourth (or hemidemisemiquaver).
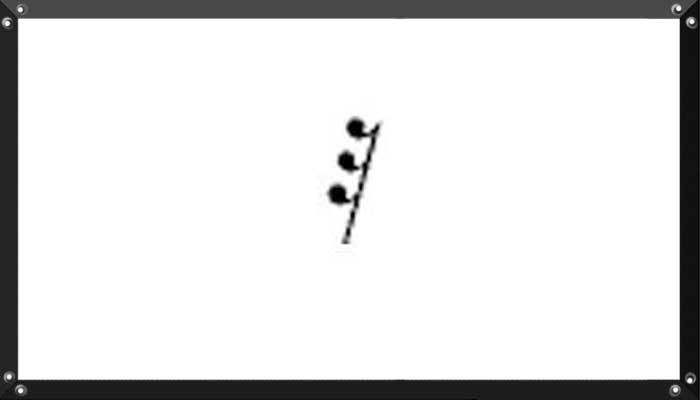

A related symbol is the thirty-second rest or demisemiquaver rest, which denotes a silence for the same duration.
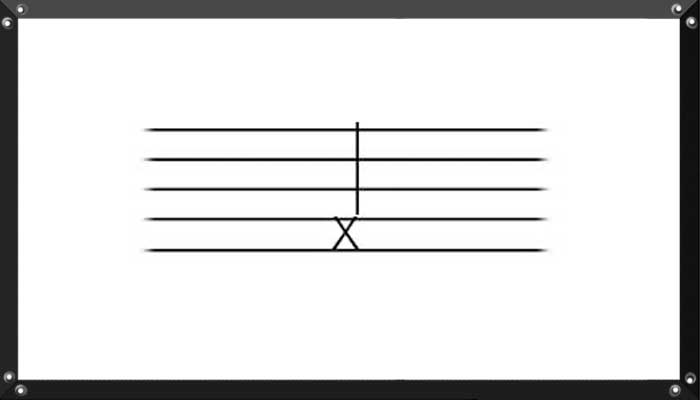
A note with a rhythmic value, but no discernible pitch when played. It is represented by a (saltire) cross (similar to the letter x) for a note head instead of an oval.
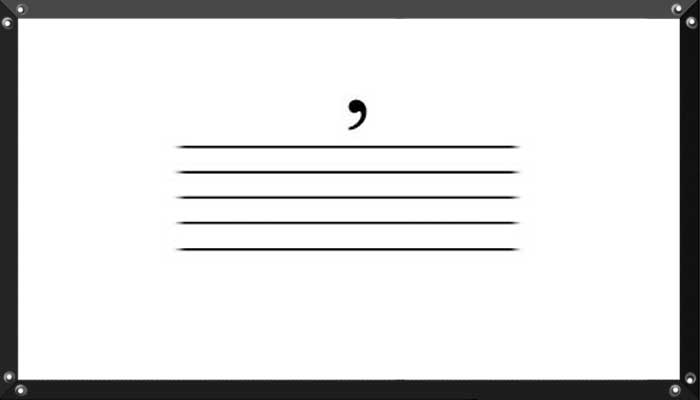

In a score, this symbol tells the performer to take a breath (or make a slight pause for non-wind instruments). This pause usually does not affect the overall tempo. For bowed instruments, it indicates to lift the bow and play the next note with a downward (or upward, if marked) bow.

Review of Music Theory 909. Now it's time to have your first Music Theory test. Let's see if you are learning and how much you know.